Self-Evaluation
1. What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of?
I thought my compendium reviews for this unit were both more organized and better written then last unit. I was also able to get good pictorials for the concepts in each sub-unit. I liked doing the major lab for this unit and I think the final published blog is well written and insightful. The last thing I am most proud of is getting all the assignments for this unit done on time and looking good.
2. What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement?
Well the first thing I could have improved on is the quiz for the fist major topic. I took this quiz and swear I answered all the questions, but when I had the quiz graded the results showed I did not answer not one, but two of the questions. I think this is crap, so for the next unit I am going to pay particular attention to the quizzes and my answers. Well for the second issue with my work nothing in particular comes to mind, I am pleased with all the assignments I have posted for this unit.
3. What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit?
I think the assignments I turned in for this unit are A quality. I would like to get an overall grade of and A for this class so a high score for this unit will be a boost.
4. How could I perform better in the next unit?
I still think my biggest done fall is my procrastination and time management skills. I did do a good job of getting an early jump on the chapters, but then I procrastinated till the end of the unit. Even though my assignments are still good, I did have to do the usual time crunch this last week to make sure everything looked good. This is still why I am looking forward to taking classes in person to put less stress on my own time issues.
REGARDING THE UNIT (adapted from Stephen Brookfield, University of St. Thomas "Critical Incident Questionnaire")
At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course?
I felt I was grasping the concepts of this chapter when I was working on the lab project and making correlations between excersing and metabolic rates.
At what moment unit did you feel most distanced from the course?
During the second week of this unit when I had some vacation which I enjoyed and did not put any time towards my assignments.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit that find most affirming and helpful?
(NA)
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing?
(NA)
What about this unit surprised you the most? (This could be something about your own reactions to the course, something that someone did, or anything else that occurs to you.)
I was surprised that even though I stay in shape by working out and taking martial arts classes I can not run worth crap, and I used to be good at running. So I guess I am not surprised that running was a little rough for me since I have not actively run in a year, but I really was dragging during the running portion of the lab, something I will have to improve on.
Monday, March 24, 2008
Sunday, March 23, 2008
Compendium Review Ch.8
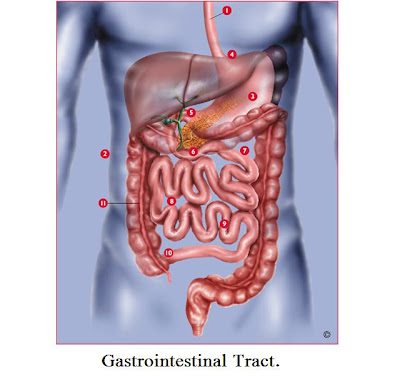 Digestion: The process of digestion is both mechanical and chemical when food is broken down into smaller pieces before it moves from the mouth to the esophagus and into the stomach it is mechanical digestion. When enzymes in the stomach and other digestion muscles break down the smaller chunks of food into its component parts its chemical digestion. When food enters the body and is digested it is going threw the process in the gastrointestinal tract (GI). The GI has four layers that make the GI wall where food passes threw, the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and the serosa.
Digestion: The process of digestion is both mechanical and chemical when food is broken down into smaller pieces before it moves from the mouth to the esophagus and into the stomach it is mechanical digestion. When enzymes in the stomach and other digestion muscles break down the smaller chunks of food into its component parts its chemical digestion. When food enters the body and is digested it is going threw the process in the gastrointestinal tract (GI). The GI has four layers that make the GI wall where food passes threw, the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and the serosa. Mouth: The primary function of the mouth and its components is to divide food into smaller pieces and then force it from the mouth into the esophagus. The mouth consists of the hard palate, nasopharynx passage, soft palate, epiglottis and glottis, and the trachea. When you swallow food is pushed to the back of the throat by the tongue. When the food slides down the esophagus the other passageways are blocked off to prevent food from going where it should not.
Mouth: The primary function of the mouth and its components is to divide food into smaller pieces and then force it from the mouth into the esophagus. The mouth consists of the hard palate, nasopharynx passage, soft palate, epiglottis and glottis, and the trachea. When you swallow food is pushed to the back of the throat by the tongue. When the food slides down the esophagus the other passageways are blocked off to prevent food from going where it should not.Pharynx: Is the passageway that food enters when it is swallowed and the intermediary between the mouth and the esophagus.
 Esophagus: the esophagus connects the food being broken down in the mouth to the stomach where it first begins to be chemically broken down. The esophagus is a long tube in the body where the wall can constrict when you swallow and force food down the stomach called the peristaltic wave.
Esophagus: the esophagus connects the food being broken down in the mouth to the stomach where it first begins to be chemically broken down. The esophagus is a long tube in the body where the wall can constrict when you swallow and force food down the stomach called the peristaltic wave. Stomach: The stomach organ sits right below the diaphragm and is the first stop of the food in the lower body. The stomach consits of the usual four layers of the GI but has modifications to the muscularis layer as well as another layer which allows the stomach to expand and contract. In stomach contains the pyloric sphincter which blocks food from leaving the stomach until it has been processed enough for the next stage. The stomach fluid is made mostly of chyme which helps control the breakdown of food.
Stomach: The stomach organ sits right below the diaphragm and is the first stop of the food in the lower body. The stomach consits of the usual four layers of the GI but has modifications to the muscularis layer as well as another layer which allows the stomach to expand and contract. In stomach contains the pyloric sphincter which blocks food from leaving the stomach until it has been processed enough for the next stage. The stomach fluid is made mostly of chyme which helps control the breakdown of food.Small intestine: The small intestine has a smaller diameter then the large intestine but the is much longer then the large intestine. In the small intestine the digestion of food by the enzymes secreated by the pancreas and bile form the gallbladder make quick work of the food particles. The small intestine wall also absorbs nutrients mainly sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, and glycerol for the digestive process.
Obesity and Cardiovascular disease: When people eat to much sweets which are high in surgar and fats from fried food it can lead to being obese with the additional threat of diabetes type 2 and cardiovascular disease. In diabetes the cells get so much sugar from what you eat the body produces to much insulin to break down the sugar. Over time the cells get so immune to the effects of the insulin they stop recognizing and responding the insulin diabetes is the result. They you have to inject insulin into the body to get the cells to recognize it and use it for breaking down sugars in your diet.
Accessory Organs: Pancreas, Liver, Gall bladder.
Pancreas: The pancreas uses the duodenum to deliver pancreatic juice with digestive enzymes for all types of food. Insulin is produced by the pancreas when the body needs extra to handle the sugar intake, insulin is a hormone (substance produced by one set of cells which affects another set of cells).
Pancreas: The pancreas uses the duodenum to deliver pancreatic juice with digestive enzymes for all types of food. Insulin is produced by the pancreas when the body needs extra to handle the sugar intake, insulin is a hormone (substance produced by one set of cells which affects another set of cells).
Liver: The liver is primarily used to detoxify the blood and remove any poisonous substances (like beer). Since the liver acts as a sewage plant for the body it is one of the largest major metabolic glands in the body. If the liver fails it can be life threatening to the person, and a transplant is generally needed. The liver does have amazing rebuilding capabilities, but when the rate of damage is faster then what the liver can repair you have a serious problem.
Gall bladder: The gall bladders major function is to store bile to be used in the liver and other organs. Bile breaks down fats into smaller pieces which make it easier to digest by other enzymes. If the bile in the gall bladder hardens into gallstones it can be incredibly painful until they are forced out of the body.
Gall bladder: The gall bladders major function is to store bile to be used in the liver and other organs. Bile breaks down fats into smaller pieces which make it easier to digest by other enzymes. If the bile in the gall bladder hardens into gallstones it can be incredibly painful until they are forced out of the body.
 Large intestine: The large intestine is composed of the cecum, colon, rectum and anal canal. The cecum is the first part of the large intestine and the entry point for defecation. The colon has three major parts, the ascending colon, transverse colon, and the descending colon. These three parts of the colon give it the box shape outline around the other organs. The large intestine form feces using fiber and other components. Feces are unproved parts of food we ingest and need to leave the body, for a person to stay healthy. Feces will collect in the rectum until a signal is sent to the brain to loosen the rectum and allow the feces to exit out the anus. One more note since feces are three quarters water to one part solid if you have diarrhea for an extended period of time you are dehydrating your body and will need to keep drinking fluids to prevent the problem from getting worse.
Large intestine: The large intestine is composed of the cecum, colon, rectum and anal canal. The cecum is the first part of the large intestine and the entry point for defecation. The colon has three major parts, the ascending colon, transverse colon, and the descending colon. These three parts of the colon give it the box shape outline around the other organs. The large intestine form feces using fiber and other components. Feces are unproved parts of food we ingest and need to leave the body, for a person to stay healthy. Feces will collect in the rectum until a signal is sent to the brain to loosen the rectum and allow the feces to exit out the anus. One more note since feces are three quarters water to one part solid if you have diarrhea for an extended period of time you are dehydrating your body and will need to keep drinking fluids to prevent the problem from getting worse. Obesity: The body mass index (BMI) is used to calculate a persons body fat to tell if they are at a healthy BMI or at risk for being obese. Studies have shown there is a global problem with people and children becoming obese (globosity).
Obesity: The body mass index (BMI) is used to calculate a persons body fat to tell if they are at a healthy BMI or at risk for being obese. Studies have shown there is a global problem with people and children becoming obese (globosity).Nutrients: Are components are body uses for a variety of different purposes. Energy, growth and development and cellular metabolism. Carbohydrates (sugars), proteins (amino acids), and lipids (fats, oils, cholesterol) are all nutrients which have a physiological function in the body.
Minerals: The body needs about 5 grams of each major mineral and less then 5 grams for trace minerals. Major minerals are calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chloride, and magnesium. For all minerals just like nutrients too much of any one can have negative affects on the body as with have not enough. The trace minerals are zinc, iron, copper, iodine, selenium, manganese.
Vitamins: There are 13 essential vitamins which are important to the body because we can not produce enough of them on our own, they must be included in our diet. Vitamins are organic compounds which are not carbs, fat, or protein which are body also needs constantly. Having to very little of certain vitamins can vitamin deficiency problems, likewise having to much vitamins can also be bad for you.
Metabolic Lab
Introduction:
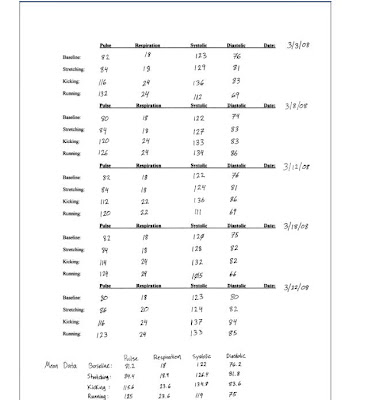
The principle of this lab is to see how our body and cardiovascular system will react as I perform different activities. I decided to do activities which I already normally do, this way the results and findings might be more meaningful to me in the future. Since I generally exercise three to four times a week, taking circulatory measurements after working out, would easily fit with my daily/weekly routine. The three activates I will perform are stretching, running, and kicking a martial arts dummy.
Hypothesis:
Since all three of my activates are doing something more then sitting on the couch I will make a general hypothesis stating: the metabolic data I collect for each activities will be different then the baseline data I will use as comparison. My understanding of the material so far in this unit tells me when I am active my pulse, breathing and blood pressure should increase to some degree or another. If I take running for instance, my heart rate should increases as my muscles need more oxygen to keep pace. If the muscles require more oxygen, then my breathing rate should increase to get more oxygen in the lungs to increase the oxygen supply for the red blood cells to transport. If the muscles need more oxygen and my heart rate and breathing increase then the heart will be pumping faster to get more red blood cells to all the active muscles. This should cause and increase in both systolic and diastolic readings. The systolic reading is measuring the pressure of the blood cells against the lining of the arteries, so if more red blood cells are moving threw the arteries then more pressure should be applied to the artery lining and this should result in increased blood pressure readings.
Stretching:
I hypothesis stretching will show the least amount of change from the base line readings of the three activities. When I am stretching I am relaxed and breathing steadily threw my nose and out my month, very similar to when I am sitting down. Even though I am doing a form of physical activity I don’t think stretching will put enough strain on the muscles to need a dramatic increase in oxygen levels. So respiration rate, pulse and both systolic and diastolic rates should be about the same as my baseline data with only slight increases.
Kicking the Kung Fu dummy:
I suspect the act of kicking the dummy for ten minutes will cause an increase in the amount of oxygen my muscles will need. I hypothesis my pulse, respiration rate, systolic and diastolic rates will all increase after ten minutes of kicking. I expect my respiration rate to change only slightly from my normal breathing rate. The reason is like stretching when I kick the dummy I am keeping my breathing controlled and even though it is physical activity and I can work up a good workout form practicing on the dummy, I think it will take more then 10 minutes to accomplish a dramatic increase in respiration. So the hypothesis is pulse, systolic, and diastolic rate will increase a noticeable amount and respiratory rate will increase slightly.
Running:
I think running for ten minutes will give me the largest change in data from the baseline. When I run I am working harder then normal and I am not a very good runner. If I am working harder then normal my body is working hard to maintain an internal constant temp (homeostasis). The sweat indicates the body needs to get rid of the increase in temperature in some form and sweating is the best way to maintain body heat, and I can easily sweat a pool after just a few minutes of running. As I run my thigh muscles get tight and tired from the activity. If the muscles are getting tired from running and normally they are not tired or tight when I am just walking then my body must be working hard to keep them going and loosing the battle. I know the body is working harder because my respiratory rate increases as I run. If my breathing is increased then my pulse should also go up because the heart will be working overtime to get red blood cells and oxygen to the leg muscles. If the rest of my body is working hard then my blood pressure should be increasing significantly. My Hypothesis for running is you will see all four measurements increase by the largest numbers compared to the baseline data.
Methods:
In order to keep the data as consistent as possible I tried to do the same procedure each time for all three activities all five days. I performed the activates and took the body measurements on my days off where I could plan ahead and not have anything else interfere with my process. For my baseline measurements I would record the data about an hour after I first woke up in the morning. I did this because I figured when I first wake up my body would be at its most relaxing and consistent state and therefore I would get consistent readings on all five days. The next step was going to the park and starting the stretching activity. Each day I would do the same stretches in the same order for an average of about ten minutes. I brought my blood pressure monitor with me to record the systolic and diastolic data as soon as practical, normally within a few minutes of finishing the stretches. Next I would walk around and warm up for about 15 minutes or so between the time I did my stretching and started my run. I wanted a little time in between the two activities so any major jumps in the data from stretching would be back to normal prior to starting the run. I tried to consistently take my four readings as soon as possible when I finished ten minutes of running, again I had the blood pressure device right there so it was normally done with in a few minutes. The stretching and running were normally done late morning about 11am or so. I take martial arts classes in the evening so I would spend the rest of the afternoon doing whatever else there was to do and about an hour before my class started I would go outside with a stop watch and kick the kung fu dummy for ten straight minutes, again as with the stretching and running I tried to get the data recorded within a few minutes of completing the exercise. By following this procedure on all five days and doing as closely as possible the exact same activities I was hoping to minimize any additional variables there might be which could alter the data.
The equipment I used to take my blood pressure was a device my roommate had and came in very handy. It is a small self contained unit with a digital readout. The device is called a Omron Blood Pressure Monitor HEM-601 (see picture). For taking my pulse I used the carotid artery under the jaw on the neck (see picture). I felt for the artery and then counted the number of pulses for 30 seconds. After 30 seconds I took the number I had and multiplied it by 2, to give me the pulse for a full minute. I did this same procedure for measuring my respiratory rate, timed 30 seconds and counted the number of breaths, then multiplying by 2 to give me the number of breaths in a full minute. (The pictures with associated captions are on a separate blog entry at the end of this report.)
Analysis:
My hypothesis for predicting the results of my metabolic rates after certain activities was not entirely unproven, however it was not 100% confirmed either. The baseline data I think was very consistent and did set a good foundation for comparing the rest of the results. As you can see in the graph (next blog entry at end of this report) my hypothesis for how dramatically my metabolic rates would change when I did basic stretching was confirmed by the data I have. You can see the color representing stretching closely follows the baseline data and is only slightly higher on average, which is what I hypothesized. The color representing kicking was also very accurate to what I hypothesized would happen. All the metabolic data for stretching were confirmed to be higher then the baseline data. As I expend energy to kick the dummy my metabolic rates go up to keep my body in a higher gear of performance. This is exactly what I thought would happen and I was happy to see the data and graph reflect my initial hypothesis. The last activity for this lab was the one which resulted in data that was somewhat confounding. The initial pulse and respiration data confirmed the body was working harder then during times when the baseline data was taken. The problem I encountered was on more then one occasion the data I collected for systolic and diastolic pressure was less then the baseline data. I know my body was working harder then normal because my pulse and respiration rate were higher then normal. The systolic and diastolic pressure however do not back up that conclusion. My hypothesis for predicting the outcome of metabolic data for running was not proven and the actual results leave question to be answered.
Problems:
Here is some of the issues I encountered while trying to accurately get consistent metabolic rates. The primary issue is variables which may have an impact on the data but are hard to eliminate. Environmental impacts, my three activities were all performed outside and while some days were pleasant and warm other days were less then desirable. I believe changes in weather conditions could have an impact on the data, but since we are under time limitations I had to collect data on the specific days I was available. In general the average temperature while I was performing the activities were in the low 60’s. There were however two days where the weather was much colder and rainier, and I suspect this could have a specific impact on the running data. The second issue would be my diet. I think I have learned enough in this unit to say confidently depending on what I had eaten or did not eat prior to running and stretching could cause some changes in the data I would get. I know some foods would give me more energy before I went running and therefore have favorable results with the data, and opposite of this some foods, like that star bucks coffee and sausage sandwich I had one time before stretching and running many not have given my body the best chance for performing its best. The third reason I may have gotten conflicting data while running is everyone’s physiology is a little bit different then the next person. What consistently happens to one person every time they perform an activity may have a slightly different affect for someone else doing the same activity. The last possible problem which may have influence my data was the actual procedure for taking the systolic and diastolic measurements. As you can see in the picture when I was done running I used the bench and quickly took my blood pressure. The device and my wrist were both below my heart when the measurements were being taken. After I had collected all my data and was calculating the results my roommate decided he would try taking his blood pressure. He actually read all the directions and it turns out when taking your blood pressure your wrist should be at heart level. You can see in my picture my wrist is well below heart level. I do not know how much of an impact this procedure would make on my results but it might be a clue for the unreliable readings I had. These are just the primary concerns I had for the accuracy of the data I collected. There are probably a few others factors which could have influenced the data that I am not addressing.
Conclusion:
In conclusion I think the data still largely supports the general hypothesis stating when we expend energy to do activities the body and heart needs to work harder to get the blood and oxygen to all the right places. When we run or participate in vigorous athletic activates the body has to work overtime to keep up with our demands for energy. This will cause the heart to beat faster , your breathing to become more labored and your blood pressure to increase as the body works harder. As for the scientific method I learned a great deal about the different variables which can have adverse affects on the data you try to collect. If I was to do another experiment like this one I would want to do many more trials (like a one hundred) then just 5 to get better well rounded data. I would also say it would be more accurate to have another person take the metabolic measurements, maybe someone even trained in proper procedures. This way you could be sure to limit as many of the variables as possible to get accurate information and a reliable analysis of the data.
The principle of this lab is to see how our body and cardiovascular system will react as I perform different activities. I decided to do activities which I already normally do, this way the results and findings might be more meaningful to me in the future. Since I generally exercise three to four times a week, taking circulatory measurements after working out, would easily fit with my daily/weekly routine. The three activates I will perform are stretching, running, and kicking a martial arts dummy.
Hypothesis:
Since all three of my activates are doing something more then sitting on the couch I will make a general hypothesis stating: the metabolic data I collect for each activities will be different then the baseline data I will use as comparison. My understanding of the material so far in this unit tells me when I am active my pulse, breathing and blood pressure should increase to some degree or another. If I take running for instance, my heart rate should increases as my muscles need more oxygen to keep pace. If the muscles require more oxygen, then my breathing rate should increase to get more oxygen in the lungs to increase the oxygen supply for the red blood cells to transport. If the muscles need more oxygen and my heart rate and breathing increase then the heart will be pumping faster to get more red blood cells to all the active muscles. This should cause and increase in both systolic and diastolic readings. The systolic reading is measuring the pressure of the blood cells against the lining of the arteries, so if more red blood cells are moving threw the arteries then more pressure should be applied to the artery lining and this should result in increased blood pressure readings.
Stretching:
I hypothesis stretching will show the least amount of change from the base line readings of the three activities. When I am stretching I am relaxed and breathing steadily threw my nose and out my month, very similar to when I am sitting down. Even though I am doing a form of physical activity I don’t think stretching will put enough strain on the muscles to need a dramatic increase in oxygen levels. So respiration rate, pulse and both systolic and diastolic rates should be about the same as my baseline data with only slight increases.
Kicking the Kung Fu dummy:
I suspect the act of kicking the dummy for ten minutes will cause an increase in the amount of oxygen my muscles will need. I hypothesis my pulse, respiration rate, systolic and diastolic rates will all increase after ten minutes of kicking. I expect my respiration rate to change only slightly from my normal breathing rate. The reason is like stretching when I kick the dummy I am keeping my breathing controlled and even though it is physical activity and I can work up a good workout form practicing on the dummy, I think it will take more then 10 minutes to accomplish a dramatic increase in respiration. So the hypothesis is pulse, systolic, and diastolic rate will increase a noticeable amount and respiratory rate will increase slightly.
Running:
I think running for ten minutes will give me the largest change in data from the baseline. When I run I am working harder then normal and I am not a very good runner. If I am working harder then normal my body is working hard to maintain an internal constant temp (homeostasis). The sweat indicates the body needs to get rid of the increase in temperature in some form and sweating is the best way to maintain body heat, and I can easily sweat a pool after just a few minutes of running. As I run my thigh muscles get tight and tired from the activity. If the muscles are getting tired from running and normally they are not tired or tight when I am just walking then my body must be working hard to keep them going and loosing the battle. I know the body is working harder because my respiratory rate increases as I run. If my breathing is increased then my pulse should also go up because the heart will be working overtime to get red blood cells and oxygen to the leg muscles. If the rest of my body is working hard then my blood pressure should be increasing significantly. My Hypothesis for running is you will see all four measurements increase by the largest numbers compared to the baseline data.
Methods:
In order to keep the data as consistent as possible I tried to do the same procedure each time for all three activities all five days. I performed the activates and took the body measurements on my days off where I could plan ahead and not have anything else interfere with my process. For my baseline measurements I would record the data about an hour after I first woke up in the morning. I did this because I figured when I first wake up my body would be at its most relaxing and consistent state and therefore I would get consistent readings on all five days. The next step was going to the park and starting the stretching activity. Each day I would do the same stretches in the same order for an average of about ten minutes. I brought my blood pressure monitor with me to record the systolic and diastolic data as soon as practical, normally within a few minutes of finishing the stretches. Next I would walk around and warm up for about 15 minutes or so between the time I did my stretching and started my run. I wanted a little time in between the two activities so any major jumps in the data from stretching would be back to normal prior to starting the run. I tried to consistently take my four readings as soon as possible when I finished ten minutes of running, again I had the blood pressure device right there so it was normally done with in a few minutes. The stretching and running were normally done late morning about 11am or so. I take martial arts classes in the evening so I would spend the rest of the afternoon doing whatever else there was to do and about an hour before my class started I would go outside with a stop watch and kick the kung fu dummy for ten straight minutes, again as with the stretching and running I tried to get the data recorded within a few minutes of completing the exercise. By following this procedure on all five days and doing as closely as possible the exact same activities I was hoping to minimize any additional variables there might be which could alter the data.
The equipment I used to take my blood pressure was a device my roommate had and came in very handy. It is a small self contained unit with a digital readout. The device is called a Omron Blood Pressure Monitor HEM-601 (see picture). For taking my pulse I used the carotid artery under the jaw on the neck (see picture). I felt for the artery and then counted the number of pulses for 30 seconds. After 30 seconds I took the number I had and multiplied it by 2, to give me the pulse for a full minute. I did this same procedure for measuring my respiratory rate, timed 30 seconds and counted the number of breaths, then multiplying by 2 to give me the number of breaths in a full minute. (The pictures with associated captions are on a separate blog entry at the end of this report.)
Analysis:
My hypothesis for predicting the results of my metabolic rates after certain activities was not entirely unproven, however it was not 100% confirmed either. The baseline data I think was very consistent and did set a good foundation for comparing the rest of the results. As you can see in the graph (next blog entry at end of this report) my hypothesis for how dramatically my metabolic rates would change when I did basic stretching was confirmed by the data I have. You can see the color representing stretching closely follows the baseline data and is only slightly higher on average, which is what I hypothesized. The color representing kicking was also very accurate to what I hypothesized would happen. All the metabolic data for stretching were confirmed to be higher then the baseline data. As I expend energy to kick the dummy my metabolic rates go up to keep my body in a higher gear of performance. This is exactly what I thought would happen and I was happy to see the data and graph reflect my initial hypothesis. The last activity for this lab was the one which resulted in data that was somewhat confounding. The initial pulse and respiration data confirmed the body was working harder then during times when the baseline data was taken. The problem I encountered was on more then one occasion the data I collected for systolic and diastolic pressure was less then the baseline data. I know my body was working harder then normal because my pulse and respiration rate were higher then normal. The systolic and diastolic pressure however do not back up that conclusion. My hypothesis for predicting the outcome of metabolic data for running was not proven and the actual results leave question to be answered.
Problems:
Here is some of the issues I encountered while trying to accurately get consistent metabolic rates. The primary issue is variables which may have an impact on the data but are hard to eliminate. Environmental impacts, my three activities were all performed outside and while some days were pleasant and warm other days were less then desirable. I believe changes in weather conditions could have an impact on the data, but since we are under time limitations I had to collect data on the specific days I was available. In general the average temperature while I was performing the activities were in the low 60’s. There were however two days where the weather was much colder and rainier, and I suspect this could have a specific impact on the running data. The second issue would be my diet. I think I have learned enough in this unit to say confidently depending on what I had eaten or did not eat prior to running and stretching could cause some changes in the data I would get. I know some foods would give me more energy before I went running and therefore have favorable results with the data, and opposite of this some foods, like that star bucks coffee and sausage sandwich I had one time before stretching and running many not have given my body the best chance for performing its best. The third reason I may have gotten conflicting data while running is everyone’s physiology is a little bit different then the next person. What consistently happens to one person every time they perform an activity may have a slightly different affect for someone else doing the same activity. The last possible problem which may have influence my data was the actual procedure for taking the systolic and diastolic measurements. As you can see in the picture when I was done running I used the bench and quickly took my blood pressure. The device and my wrist were both below my heart when the measurements were being taken. After I had collected all my data and was calculating the results my roommate decided he would try taking his blood pressure. He actually read all the directions and it turns out when taking your blood pressure your wrist should be at heart level. You can see in my picture my wrist is well below heart level. I do not know how much of an impact this procedure would make on my results but it might be a clue for the unreliable readings I had. These are just the primary concerns I had for the accuracy of the data I collected. There are probably a few others factors which could have influenced the data that I am not addressing.
Conclusion:
In conclusion I think the data still largely supports the general hypothesis stating when we expend energy to do activities the body and heart needs to work harder to get the blood and oxygen to all the right places. When we run or participate in vigorous athletic activates the body has to work overtime to keep up with our demands for energy. This will cause the heart to beat faster , your breathing to become more labored and your blood pressure to increase as the body works harder. As for the scientific method I learned a great deal about the different variables which can have adverse affects on the data you try to collect. If I was to do another experiment like this one I would want to do many more trials (like a one hundred) then just 5 to get better well rounded data. I would also say it would be more accurate to have another person take the metabolic measurements, maybe someone even trained in proper procedures. This way you could be sure to limit as many of the variables as possible to get accurate information and a reliable analysis of the data.
Saturday, March 22, 2008
I love happy meals, but they dont love me
After reading the material for this unit I have developed some ideas about dieting and how society is being affected by the media and food corporations. This essay gives me the opportunity to talk about the research I have done from the web (class web links) but also to interject my personal concerns, like everyone I have an opinion on the subject and I think I will be able to adequately defend my opinions. I read the article posted on the New York times by Michael Pollan, and for the most part many of my opinions about our current dieting crisis is also expressed in Pollan’s extensive article on the subject. Pollan‘s paper “unhappy meals“ was incredibly insightful and informative to many of the dieting problems Americans face.
After reading Pollan’s article I did feel somewhat enlightened on the subject of dieting and why there are so many different diets out there, which seem to have very little affect. The causes and reasons for this are very eloquently explained in plain language by Mr. Pollan. Pollan address the media one of the primary culprits for misleading people about dieting. I can relate to his sentiments, I absolutely hate watching the phoenix suns basketball game and during a timeout the broadcast cuts to commercials advertising the newest miracle breakthrough in dieting. The current crisis we as a society are facing with obesity and related illnesses can in large part be blamed on the media and how they portray the food industry. During the same commercial break we as viewers can see the next fantastic tasting hamburger from Jack in the Box which we know is not healthy for us, so after we eat this monstrosity the next commercial will show us the magic pill we can take to loose the weight we just gained. Of course not all of the blame can go on the media or the food industry, we as a society need to take some personal responsibility for what we eat and what media advertisements we should believe.
I have had numerous friends over the years (most of them female) who have tried different weight loss programs with mixed disappointing results. After reading Pollan’s article the problem with these systems is clear, many of these gimmick pills have very little health value associated with them. Having a celebrity or someone with presumed authority on the subject (Dr. Who) does not guarantee results, we as the public try these trendy programs and then wonder why 6 months from now we are still at the same weight, discouraged, and a little poorer in the pocket book. If you open any popular magazine in the supermarket you can find numerous weight loss pills and programs. If I was someone trying to lose weight I would be overwhelmed by the countless and confusing weight loss solutions I should try. When in fact the true answer to loosing weight is so much simpler and not found in the supermarket or GNC.
Eating a vegetable based diet with meat as a side dish instead of the main dish would be a great start. Buying produce from a fresh farmers market instead of processed food would be a second good idea. Eating in moderation when you are really hungry and not just to eat would cut down on your food intake. If you did a few of these suggestions and then throw in a little exercise here and there I think the results as a society would be incredibly more successful. But how can food corporations and the media make a profit on such simple advice. From what I have seen I don’t even think you need to give up everything you like to eat to make weight loss or eating healthier successful. For any given week if you said I am going to attempt to eat better following some of these suggestions and then for one day I will eat something not healthy that I really like (pizza, chips, beer) you should still be able to maintain a healthier diet. The alternative would be to stay with a specific confusing dieting regiment and have to fight your urge to binge eat on foods you really want. Either way you are going to eat that piece of pizza, so why not just work it in to you weekly eating habits. According to Pollan the simple idea of eating less meat and more vegetables and greens has been around for a long time and is known to significantly help with obesity and related problems, but the media, food manufactures, and nutrionists have done a great job in keeping it under wraps and marketing there own products as the miracle cure.
One of the web links which I thought was also very insightful was the farm to school web page. As a culture kids will follow the eating habits of the parents. If your parents are eating mostly processed food and supermarket bargains then there kids will also probably develop those habits as well. In Washington state in 2002 the Washington legislature directed the Washington state department of agriculture to promote programs in the community to enhance local produce and educational outreach programs like farm to school. In my opinion if more education can be given to kids on how to properly prepare meals and avoid fast food items then there is a chance future generations could overcome the current obesity epidemic.
I agree with the notion that as a culture we have lost the pleasure of cooking a family meal at home and actually enjoying good quality meals. Are generally faced paced lives make it harder to slow down and do things like prepare meals for the family, especially when convince tells you to get some KFC from the drive threw. There seems to be no doubt at least in my mind that a meal prepared at home with fresh local produce will have a significant amount of vitamins, minerals and nutrients which processed and fast foods do not. For me personally the best example I can use is my grandparents. They are both in there early 70’s and my grandma makes a mean meal, nothing fancy or complicated but home cooking with generally some meat with vegetables and a salad. Every time I visit them I look forward to breakfast and dinner. Now a nutrionist might say they are eating to much saturated fat foods or not getting some of the vitamins they should get if they take a supplement. I would argue that they have been eating there diverse local cuisine for some 30 years (since I have been alive) and they are both in excellent health and have not had any complications with cardiovascular disease or cancer. My grandpa at 70 something still works the ranch everyday (daily exercise) as is still built like a bull. So mixing a well rounded diet without the abundance of processed food and more greens in your diet with a little amount of daily activity could keep you in fairly good shape, is this not what people have done for the last couple hundred years until our generation.
In conclusion the solution to an obese society that is constantly battling health problems may not be in any miracle pill or complicated dieting solutions. Maybe eating good tasting locally made and prepared foods with all the natural ingredients already included and some moderate exercise during the week will help to turn our media driven diet around. I would like to start eating healthier and I think my first step will be to eat smaller meals when I am actually hungry with some snacks in between and have my meals be less focused on meat products and more on greens. I already have the frequent exercise covered and I have found some markets in my area which support and sell locally grown produce. Following some of these simple steps I hope to prevent my self from developing health complications as I get older and join the middle age club.
After reading Pollan’s article I did feel somewhat enlightened on the subject of dieting and why there are so many different diets out there, which seem to have very little affect. The causes and reasons for this are very eloquently explained in plain language by Mr. Pollan. Pollan address the media one of the primary culprits for misleading people about dieting. I can relate to his sentiments, I absolutely hate watching the phoenix suns basketball game and during a timeout the broadcast cuts to commercials advertising the newest miracle breakthrough in dieting. The current crisis we as a society are facing with obesity and related illnesses can in large part be blamed on the media and how they portray the food industry. During the same commercial break we as viewers can see the next fantastic tasting hamburger from Jack in the Box which we know is not healthy for us, so after we eat this monstrosity the next commercial will show us the magic pill we can take to loose the weight we just gained. Of course not all of the blame can go on the media or the food industry, we as a society need to take some personal responsibility for what we eat and what media advertisements we should believe.
I have had numerous friends over the years (most of them female) who have tried different weight loss programs with mixed disappointing results. After reading Pollan’s article the problem with these systems is clear, many of these gimmick pills have very little health value associated with them. Having a celebrity or someone with presumed authority on the subject (Dr. Who) does not guarantee results, we as the public try these trendy programs and then wonder why 6 months from now we are still at the same weight, discouraged, and a little poorer in the pocket book. If you open any popular magazine in the supermarket you can find numerous weight loss pills and programs. If I was someone trying to lose weight I would be overwhelmed by the countless and confusing weight loss solutions I should try. When in fact the true answer to loosing weight is so much simpler and not found in the supermarket or GNC.
Eating a vegetable based diet with meat as a side dish instead of the main dish would be a great start. Buying produce from a fresh farmers market instead of processed food would be a second good idea. Eating in moderation when you are really hungry and not just to eat would cut down on your food intake. If you did a few of these suggestions and then throw in a little exercise here and there I think the results as a society would be incredibly more successful. But how can food corporations and the media make a profit on such simple advice. From what I have seen I don’t even think you need to give up everything you like to eat to make weight loss or eating healthier successful. For any given week if you said I am going to attempt to eat better following some of these suggestions and then for one day I will eat something not healthy that I really like (pizza, chips, beer) you should still be able to maintain a healthier diet. The alternative would be to stay with a specific confusing dieting regiment and have to fight your urge to binge eat on foods you really want. Either way you are going to eat that piece of pizza, so why not just work it in to you weekly eating habits. According to Pollan the simple idea of eating less meat and more vegetables and greens has been around for a long time and is known to significantly help with obesity and related problems, but the media, food manufactures, and nutrionists have done a great job in keeping it under wraps and marketing there own products as the miracle cure.
One of the web links which I thought was also very insightful was the farm to school web page. As a culture kids will follow the eating habits of the parents. If your parents are eating mostly processed food and supermarket bargains then there kids will also probably develop those habits as well. In Washington state in 2002 the Washington legislature directed the Washington state department of agriculture to promote programs in the community to enhance local produce and educational outreach programs like farm to school. In my opinion if more education can be given to kids on how to properly prepare meals and avoid fast food items then there is a chance future generations could overcome the current obesity epidemic.
I agree with the notion that as a culture we have lost the pleasure of cooking a family meal at home and actually enjoying good quality meals. Are generally faced paced lives make it harder to slow down and do things like prepare meals for the family, especially when convince tells you to get some KFC from the drive threw. There seems to be no doubt at least in my mind that a meal prepared at home with fresh local produce will have a significant amount of vitamins, minerals and nutrients which processed and fast foods do not. For me personally the best example I can use is my grandparents. They are both in there early 70’s and my grandma makes a mean meal, nothing fancy or complicated but home cooking with generally some meat with vegetables and a salad. Every time I visit them I look forward to breakfast and dinner. Now a nutrionist might say they are eating to much saturated fat foods or not getting some of the vitamins they should get if they take a supplement. I would argue that they have been eating there diverse local cuisine for some 30 years (since I have been alive) and they are both in excellent health and have not had any complications with cardiovascular disease or cancer. My grandpa at 70 something still works the ranch everyday (daily exercise) as is still built like a bull. So mixing a well rounded diet without the abundance of processed food and more greens in your diet with a little amount of daily activity could keep you in fairly good shape, is this not what people have done for the last couple hundred years until our generation.
In conclusion the solution to an obese society that is constantly battling health problems may not be in any miracle pill or complicated dieting solutions. Maybe eating good tasting locally made and prepared foods with all the natural ingredients already included and some moderate exercise during the week will help to turn our media driven diet around. I would like to start eating healthier and I think my first step will be to eat smaller meals when I am actually hungry with some snacks in between and have my meals be less focused on meat products and more on greens. I already have the frequent exercise covered and I have found some markets in my area which support and sell locally grown produce. Following some of these simple steps I hope to prevent my self from developing health complications as I get older and join the middle age club.
Wednesday, March 12, 2008
Food for a day.

 -How healthy a daily diet do you think this is? Why?
-How healthy a daily diet do you think this is? Why?Looking at the foods I eat currently and the types of food I could be eating my current diet is probably not the most healthiest for me. I would like to say that I don’t eat that much junk food on average, but there are some weeks where I eat almost no fast food (breakfast burritos) and actually eat some what healthy. Then there are other weeks where I do end up eating more processed and fast food then I should.
 -What would you change about this day's eating, if anything?
-What would you change about this day's eating, if anything?Well I really don’t have any plans to not eat this type of food. I love having eating pizza probably once a week or so along with other pastas. I eat breakfast burritos on occasion because I run out of breakfast foods at home and want to get something before I go to work. The cola I have an addiction for. So to keep my addiction in check I normally only have one can of coke a day and sometimes I will cut that out on the weekends. On the weekends I replace the Coke Cola with beer so I don’t think I am getting any extra points with that trade.
-Do you find this kind of nutritional tracking helpful? Why or why not?
I think some of those websites are helpful if you are someone who is attempting to track you food intake. I am currently at the stage in my life where I am still very active and athletic so I don’t really worry to much about what type of food I eat right now. I do however keep in mind that there will be a point in my future where I will need to start watching not only what I eat and drink but also how much exercise I may need to stay fit. I feel this time is still a long day over the horizon and not something I need to concern myself with right now. I have been eating not so healthy food since high school and my metabolism works in such a way I have not lost or gained more then 5-8lbs in some 10 years or so. So I feel pretty confident I can handle these future challenges in stride when they occur.
 I used the Body mass index from one of the websites to test my theory that I can still eat what I want and maintain a constant physique. Based on the body mass index, I am placed at the lower end of the body mass index scale for someone of my height. I think this little test some what validates that I can still eat foods that are not healthy as long as I maintain a constant active lifestyle. If at some point I stop doing the activities which keep me in shape I have no doubt I will start having to watch what I eat.
I used the Body mass index from one of the websites to test my theory that I can still eat what I want and maintain a constant physique. Based on the body mass index, I am placed at the lower end of the body mass index scale for someone of my height. I think this little test some what validates that I can still eat foods that are not healthy as long as I maintain a constant active lifestyle. If at some point I stop doing the activities which keep me in shape I have no doubt I will start having to watch what I eat.
I think some of those websites are helpful if you are someone who is attempting to track you food intake. I am currently at the stage in my life where I am still very active and athletic so I don’t really worry to much about what type of food I eat right now. I do however keep in mind that there will be a point in my future where I will need to start watching not only what I eat and drink but also how much exercise I may need to stay fit. I feel this time is still a long day over the horizon and not something I need to concern myself with right now. I have been eating not so healthy food since high school and my metabolism works in such a way I have not lost or gained more then 5-8lbs in some 10 years or so. So I feel pretty confident I can handle these future challenges in stride when they occur.
 I used the Body mass index from one of the websites to test my theory that I can still eat what I want and maintain a constant physique. Based on the body mass index, I am placed at the lower end of the body mass index scale for someone of my height. I think this little test some what validates that I can still eat foods that are not healthy as long as I maintain a constant active lifestyle. If at some point I stop doing the activities which keep me in shape I have no doubt I will start having to watch what I eat.
I used the Body mass index from one of the websites to test my theory that I can still eat what I want and maintain a constant physique. Based on the body mass index, I am placed at the lower end of the body mass index scale for someone of my height. I think this little test some what validates that I can still eat foods that are not healthy as long as I maintain a constant active lifestyle. If at some point I stop doing the activities which keep me in shape I have no doubt I will start having to watch what I eat.Monday, March 10, 2008
Thursday, March 6, 2008
Compendium Review Unit II Ch. 5,6,7
 Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular SystemThe main purpose of the cardiovascular system is to provide a route for blood to penetrate every organ and tissue in the body. Using an analogy of roads the main route for blood to move threw the body are the arteries and veins from and to the heart. These are the freeways of the body, the artery takes oxygen rich blood from the heart and drops the blood off at intersections to highways called arterioles. The Veins take blood from the highways called venule’s where oxygen deprived and carbon monoxide and waste rich cells travel back to the kidneys to drop off waste and then to the heart and lungs for more oxygen. Both the major freeways (artery’s, veins) flow to highways (arteriole’s and venule’s) and meet at the local streets called capillary beds which would connect to the local houses (cells, skin, tissue organs, etc). There are no organs, cells, or tissues which are ever far from a capillary bed.
The lymphatic system could be thought of as the sewer. The lymphatic system picks up tissue fluid, which becomes lymph and eventually returns it to the streets and highways.
The freeways and highways of the body are very strong and made of the same three layers. There is connective tissue, elastic tissue and then smooth tissue with the endothelium being the center. Because of these three layers blood cells and other cells can not escape these roads once they are on them. (can not diffuse out of these pathways)
The streets (capillary beds) are thin walled pathways which allows diffusion of oxygen, water, amino acids, glucose, waste and carbon dioxide.
 The heart and blood vessels (freeways, highways, and streets, sewers) are the main components of the cardiovascular system and with other organs regulate the bodies internal functions.
The heart and blood vessels (freeways, highways, and streets, sewers) are the main components of the cardiovascular system and with other organs regulate the bodies internal functions.HEART
The heart is a double pump organ. Blood enters the left atrium threw the veins and is pumped from the left side of the pump to the lungs. At the lungs the blood collects oxygen and goes to the right side of the pump and the right atrium. Now that the blood is oxygen rich it goes to the aorta the largest blood vessel in the body. From there the blood is pumped threw the arteries by pressure from the heart. The heart pumps O2 rich blood threw out the body using pressure. The carbon dioxide rich blood travels back to the heart threw the veins with the body muscles contracting to force blood up the veins where valves then shut to prevent the blood from back flowing (skeletal muscle pump).
 Actual Image of my lungs, pretty good for a camera phone.
Actual Image of my lungs, pretty good for a camera phone.
Exchanges at the capillaries
At the arteriole end of the capillary bed blood pressure is greater then osmotic pressure so water leaves the capillaries. At the venous end of the capillary bed osmotic pressure with the presence of proteins is greater then blood pressure so water enters the capillaries. In the midsection of capillary beds the blood pressure and osmotic pressure are the same so oxygen and nutrients diffuse out to tissue, and CO2 and waste diffuse in.
Systemic Circuit: Exchanges with tissue fluid
Flow of blood = left ventricle - aorta - common iliac artery - femoral artery - lower leg capillaries - femoral artery
Pulmonary circuit: exchange of gases
Blood flow threw the lungs. In the pulmonary circuit veins have O2 rich blood and arteries have CO2 rich blood, so the normal rule of O2 rich blood flow in arteries and CO2 rich blood flow in veins is opposite during the exchange of gases in the lungs.
The heart needs a constant supply of oxygen as well since it is one of the largest consumers of O2. The heart has its own set of arteries for getting blood, the coronary arteries. These arteries are the first to branch off of the aorta.
 PLATELETS AND BLOOD CLOTTING
PLATELETS AND BLOOD CLOTTING
Platelets (thrombocytes) are pieces of other cells called megakaryocytic in the red bone marrow. Platelets are essential to form a blood clotting also called coagulation.
The process: blood vessel is punctured, platelets congregate and form a plug, platelets and damaged tissue cells release prothrombin (Thrombin) activator, the fibrin threads form and trap red blood cells.
 BLOOD TYPES
BLOOD TYPES
It is extremely important to determine a persons blood type prior to a blood transfusion. If blood of a different type is injected into the body of someone with a different blood type agglutination can occur. Agglutination is the clotting of the blood when the blood antibodies attach to antigen of the new blood. This causes the blood to group together and become to large to move threw the blood vessels causing serious blood clots. There are 4 blood types. Type A blood, Type B blood, Type AB blood, and Type O blood. Type O blood is known as the universal blood because agglutination will not occur with any other blood type. In reality there are a few other types of blood which can create other complications.
Homeostasis = The blood and cardiovascular system along all the other organs in the body work efficiently together to keep the body in homeostasis. Homeostasis is the bodies natural way of maintaining a constant internal temperature, and as work is done by the muscles or other environmental conditions are encountered the bodies internal organs and blood will work to keep the bodies internal functions as stable as possible.
The heart is a double pump organ. Blood enters the left atrium threw the veins and is pumped from the left side of the pump to the lungs. At the lungs the blood collects oxygen and goes to the right side of the pump and the right atrium. Now that the blood is oxygen rich it goes to the aorta the largest blood vessel in the body. From there the blood is pumped threw the arteries by pressure from the heart. The heart pumps O2 rich blood threw out the body using pressure. The carbon dioxide rich blood travels back to the heart threw the veins with the body muscles contracting to force blood up the veins where valves then shut to prevent the blood from back flowing (skeletal muscle pump).
The cardiac cycle consists of the opening and closing of valves in the heart, designated as the working phase (systole) and the resting phase (diastole).
The pulse is how we measure how well the heart is pumping blood threw the body. There are two primary artery’s on the body used for measuring heart rate. Radial artery in the wrist and the carotid artery in the neck.
The pulse is how we measure how well the heart is pumping blood threw the body. There are two primary artery’s on the body used for measuring heart rate. Radial artery in the wrist and the carotid artery in the neck.
Blood pressure is measure two ways, the systolic pressure, the highest arterial pressure, blood being pumped from the heart, and diastolic pressure the pressure while the heart ventricles are relaxing. Blood pressure is determined by the blood being forced from the heart in the arteries, and is the blood being forced against the inside of the blood vessels.
 Actual Image of my lungs, pretty good for a camera phone.
Actual Image of my lungs, pretty good for a camera phone.Exchanges at the capillaries
At the arteriole end of the capillary bed blood pressure is greater then osmotic pressure so water leaves the capillaries. At the venous end of the capillary bed osmotic pressure with the presence of proteins is greater then blood pressure so water enters the capillaries. In the midsection of capillary beds the blood pressure and osmotic pressure are the same so oxygen and nutrients diffuse out to tissue, and CO2 and waste diffuse in.
Systemic Circuit: Exchanges with tissue fluid
Flow of blood = left ventricle - aorta - common iliac artery - femoral artery - lower leg capillaries - femoral artery
Pulmonary circuit: exchange of gases
Blood flow threw the lungs. In the pulmonary circuit veins have O2 rich blood and arteries have CO2 rich blood, so the normal rule of O2 rich blood flow in arteries and CO2 rich blood flow in veins is opposite during the exchange of gases in the lungs.
The heart needs a constant supply of oxygen as well since it is one of the largest consumers of O2. The heart has its own set of arteries for getting blood, the coronary arteries. These arteries are the first to branch off of the aorta.
RED BLOOD CELLS
Red blood cells are a good example of how evolution has allowed us to develop cells for a specific purpose. Red blood cells are only created to carry oxygen from the lungs and heart to all parts of the body and then to take waste to the liver and CO2 back to the lungs. Red blood cells have no organelles or nucleus. They do have 280 million molecules of hemoglobin which carry 4 molecules of O2.
Red blood cells are a good example of how evolution has allowed us to develop cells for a specific purpose. Red blood cells are only created to carry oxygen from the lungs and heart to all parts of the body and then to take waste to the liver and CO2 back to the lungs. Red blood cells have no organelles or nucleus. They do have 280 million molecules of hemoglobin which carry 4 molecules of O2.
Red Blood cells are produced from bone marrow at a rate of 2 million per second. They produce at this fantastic rate threw a special, simpler form of mitosis. When the body needs more RBC it produces erythropoietin in the kidneys and stem cells increase the production of RBC in bone marrow.
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
While red blood cells are designed for the cardiovascular system white blood cells are designed for the immune system and are the soldiers against disease. Unlike RBC white blood cells are larger and have a nucleus. RBC die at a rate of 250 million a minute while WBC not killed in fighting infections may live for years.
While red blood cells are designed for the cardiovascular system white blood cells are designed for the immune system and are the soldiers against disease. Unlike RBC white blood cells are larger and have a nucleus. RBC die at a rate of 250 million a minute while WBC not killed in fighting infections may live for years.
Types of White blood cells
Granular Leukocytes = White blood cells having granules like lysosomes, which contain various enzymes and proteins, these also help the WBC fight disease.
Neutrophil = 50-70% of all WBC, are like vacuum cleaners, they act as first responders to a pathogen or infection.
Eosinophil = during the event of a parasitic worm, infection, or allergic reaction they increase in number.
Basophil = release histamine to fight allergic reactions, histamine dilates blood vessels, but can also constrict the air tubes causing asthma attack or difficulty breathing.
Agranular Leukocytes = white blood cells which do not contain granulars (mononuclear leukocytes)
Lymphocyte = 25-35% of all WBC, responsible for specific immune defense. There are two types of lymphocyte B-cells and T-cells.
Monocyte = largest of WBC’s, they can become even larger macrophages and dendritic cells (vacuum cleaners)
Granular Leukocytes = White blood cells having granules like lysosomes, which contain various enzymes and proteins, these also help the WBC fight disease.
Neutrophil = 50-70% of all WBC, are like vacuum cleaners, they act as first responders to a pathogen or infection.
Eosinophil = during the event of a parasitic worm, infection, or allergic reaction they increase in number.
Basophil = release histamine to fight allergic reactions, histamine dilates blood vessels, but can also constrict the air tubes causing asthma attack or difficulty breathing.
Agranular Leukocytes = white blood cells which do not contain granulars (mononuclear leukocytes)
Lymphocyte = 25-35% of all WBC, responsible for specific immune defense. There are two types of lymphocyte B-cells and T-cells.
Monocyte = largest of WBC’s, they can become even larger macrophages and dendritic cells (vacuum cleaners)
 PLATELETS AND BLOOD CLOTTING
PLATELETS AND BLOOD CLOTTINGPlatelets (thrombocytes) are pieces of other cells called megakaryocytic in the red bone marrow. Platelets are essential to form a blood clotting also called coagulation.
The process: blood vessel is punctured, platelets congregate and form a plug, platelets and damaged tissue cells release prothrombin (Thrombin) activator, the fibrin threads form and trap red blood cells.
 BLOOD TYPES
BLOOD TYPESIt is extremely important to determine a persons blood type prior to a blood transfusion. If blood of a different type is injected into the body of someone with a different blood type agglutination can occur. Agglutination is the clotting of the blood when the blood antibodies attach to antigen of the new blood. This causes the blood to group together and become to large to move threw the blood vessels causing serious blood clots. There are 4 blood types. Type A blood, Type B blood, Type AB blood, and Type O blood. Type O blood is known as the universal blood because agglutination will not occur with any other blood type. In reality there are a few other types of blood which can create other complications.
Homeostasis = The blood and cardiovascular system along all the other organs in the body work efficiently together to keep the body in homeostasis. Homeostasis is the bodies natural way of maintaining a constant internal temperature, and as work is done by the muscles or other environmental conditions are encountered the bodies internal organs and blood will work to keep the bodies internal functions as stable as possible.
BACTERIA and VIRUSES
Bacteria = Are body composition is mostly bacteria, and bacteria is all around all the time. Most bacteria is helpful and harmless and only on occasion can bacteria become a threat. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells which do not need a host to live and can replicate themselves independently of a host unlike viruses.
Viruses = do not have a nucleus but they do have a nucleic acid core with its own DNA. Viruses need the organelles of a host cell live and reproduce. Viruses while they can not live without a host cell they can stay dormant (sleeping) until an opportunity presents itself to take a host.
Pathogens is the term for anything foreign in the body including bad bacteria and viruses which need combating.
Bacteria = Are body composition is mostly bacteria, and bacteria is all around all the time. Most bacteria is helpful and harmless and only on occasion can bacteria become a threat. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells which do not need a host to live and can replicate themselves independently of a host unlike viruses.
Viruses = do not have a nucleus but they do have a nucleic acid core with its own DNA. Viruses need the organelles of a host cell live and reproduce. Viruses while they can not live without a host cell they can stay dormant (sleeping) until an opportunity presents itself to take a host.
Pathogens is the term for anything foreign in the body including bad bacteria and viruses which need combating.
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
The lymphatic system is crucial for the development of the bodies soldiers (B-cells, T-cells) and training theses soldiers for combat. All blood cells are created in the red bone marrow, this is where the regular troops B-cells will also develop. For the special forces soldiers they need extra training and develop in the thymus gland after being created in the red bone marrow. The other organs involved are the spleen where blood is cleansed of any pathogens and debris. The lymph nodes clean the lymph fluid of pathogens and debris. The tonsils, peyer’s patches and appendix are other organs which are involved in the lymphatic system.
The lymphatic system is crucial for the development of the bodies soldiers (B-cells, T-cells) and training theses soldiers for combat. All blood cells are created in the red bone marrow, this is where the regular troops B-cells will also develop. For the special forces soldiers they need extra training and develop in the thymus gland after being created in the red bone marrow. The other organs involved are the spleen where blood is cleansed of any pathogens and debris. The lymph nodes clean the lymph fluid of pathogens and debris. The tonsils, peyer’s patches and appendix are other organs which are involved in the lymphatic system.
NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES
The body has multiple ways to protect against pathogens, the first being or skin acts as the first line of defense to invading forces. If bacteria or viruses are able to penetrate the skin due to cuts or bruises or other sources the body has an inflammatory reaction. During this reaction the area surrounding the injury will become swollen and even red, this is caused by an increase in blood flow which is bringing the troops to the battle. The Europhiles and macrophages enter threw the blood stream and immediately start to clear away cellular debris and pickup and pathogens they can attack. These defenses are called nonspecific because the soldiers are responding to any threat that enters the body. Specific defense is where specialized soldiers are called in to attack a specific pathogen. This normally occurs after an initial attack is made with nonspecific defenses, it takes a little time to mobilize the special forces for attack.
The body has multiple ways to protect against pathogens, the first being or skin acts as the first line of defense to invading forces. If bacteria or viruses are able to penetrate the skin due to cuts or bruises or other sources the body has an inflammatory reaction. During this reaction the area surrounding the injury will become swollen and even red, this is caused by an increase in blood flow which is bringing the troops to the battle. The Europhiles and macrophages enter threw the blood stream and immediately start to clear away cellular debris and pickup and pathogens they can attack. These defenses are called nonspecific because the soldiers are responding to any threat that enters the body. Specific defense is where specialized soldiers are called in to attack a specific pathogen. This normally occurs after an initial attack is made with nonspecific defenses, it takes a little time to mobilize the special forces for attack.
SPECIFIC DEFENSES
As mentioned before specific defenses uses specially trained troops to fight the pathogens called B cells and T cells, these cells are also know as B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes.
These are two types of white blood cells and both types generally fight the pathogens in the same way. First the pathogen is recognized by the B-cells which has a specific receptor that fits that particular pathogen. The B cell receptor (BCR) is DNA coded to recognize a specific pathogen. When the BCR encounters that pathogen in the blood stream it immediately starts to replicate, making exact duplicates of itself to fight the threat, this process is called clonal production. When the threat has been neutralized some of the B cells will stay in the blood stream as memory cells incase the same pathogen is present in the future. This allows for a much quicker build up of forces to attack the pathogen again. The rest of the B cells are no longer needed and will undergo cellular death called apoptosis. T cells are the biggest WBC’s and they will be called in to attack a pathogen when a macrophage using human leukocyte antigen (HLA) recognizes and pathogen is present. Once a pathogen is recognized cytotoxic T cells will coordinate the attack while the helper T cells undergo clonal expansion until the battle is won. Again like B cells most of the T cells will die while a few will become memory T cells ready for the next time the same illness is present.
As mentioned before specific defenses uses specially trained troops to fight the pathogens called B cells and T cells, these cells are also know as B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes.
These are two types of white blood cells and both types generally fight the pathogens in the same way. First the pathogen is recognized by the B-cells which has a specific receptor that fits that particular pathogen. The B cell receptor (BCR) is DNA coded to recognize a specific pathogen. When the BCR encounters that pathogen in the blood stream it immediately starts to replicate, making exact duplicates of itself to fight the threat, this process is called clonal production. When the threat has been neutralized some of the B cells will stay in the blood stream as memory cells incase the same pathogen is present in the future. This allows for a much quicker build up of forces to attack the pathogen again. The rest of the B cells are no longer needed and will undergo cellular death called apoptosis. T cells are the biggest WBC’s and they will be called in to attack a pathogen when a macrophage using human leukocyte antigen (HLA) recognizes and pathogen is present. Once a pathogen is recognized cytotoxic T cells will coordinate the attack while the helper T cells undergo clonal expansion until the battle is won. Again like B cells most of the T cells will die while a few will become memory T cells ready for the next time the same illness is present.
AQUIRED IMMUNITY
Immunization is a good example of acquired immunity. When the individual is not in any immediate threat the body can be injected with a small sample of the viruses the physician is trying to prevent. Once the body has the small viruses the B cells and T cells will start the process of specific defense. Now the body will have built its own natural troops which will be ready to quickly contain the viruses when attacked again. This is how common children’s diseases are prevented before these crippling disease can take hold (mumps, measles, polio, etc).
The second type of acquired immunity is passive immunity where the individual is already suffering from the disease. In this case the specific antibodies to fight the infection or disease is injected into the body to provide extra support to combat the pathogen. This type of immunity is only short lived since the cells are injected in as opposed to the body producing the WBC’s naturally. Taking a flu vaccination every year is a good example of acquired immunity.
Immunization is a good example of acquired immunity. When the individual is not in any immediate threat the body can be injected with a small sample of the viruses the physician is trying to prevent. Once the body has the small viruses the B cells and T cells will start the process of specific defense. Now the body will have built its own natural troops which will be ready to quickly contain the viruses when attacked again. This is how common children’s diseases are prevented before these crippling disease can take hold (mumps, measles, polio, etc).
The second type of acquired immunity is passive immunity where the individual is already suffering from the disease. In this case the specific antibodies to fight the infection or disease is injected into the body to provide extra support to combat the pathogen. This type of immunity is only short lived since the cells are injected in as opposed to the body producing the WBC’s naturally. Taking a flu vaccination every year is a good example of acquired immunity.
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS
Individuals who are hypersensitive will normally experience an immediate allergic reaction as the antibodies recognize foreign pathogens. A person could also experience a delayed reaction where it takes time for the T cells to mobilize and attack. The bodies natural defenses can also be harmful especially to individuals who need organ transplants. Before a person can receive organ transplant, care must be taken to ensure the body will not reject the foreign organ. Test are done on the individual to make sure the body will have the best chance of accepting the new organ.
Individuals who are hypersensitive will normally experience an immediate allergic reaction as the antibodies recognize foreign pathogens. A person could also experience a delayed reaction where it takes time for the T cells to mobilize and attack. The bodies natural defenses can also be harmful especially to individuals who need organ transplants. Before a person can receive organ transplant, care must be taken to ensure the body will not reject the foreign organ. Test are done on the individual to make sure the body will have the best chance of accepting the new organ.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)