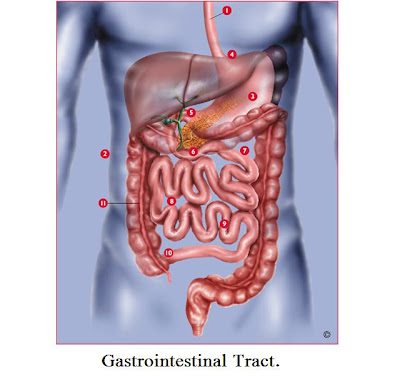
 Digestion: The process of digestion is both mechanical and chemical when food is broken down into smaller pieces before it moves from the mouth to the esophagus and into the stomach it is mechanical digestion. When enzymes in the stomach and other digestion muscles break down the smaller chunks of food into its component parts its chemical digestion. When food enters the body and is digested it is going threw the process in the gastrointestinal tract (GI). The GI has four layers that make the GI wall where food passes threw, the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and the serosa.
Digestion: The process of digestion is both mechanical and chemical when food is broken down into smaller pieces before it moves from the mouth to the esophagus and into the stomach it is mechanical digestion. When enzymes in the stomach and other digestion muscles break down the smaller chunks of food into its component parts its chemical digestion. When food enters the body and is digested it is going threw the process in the gastrointestinal tract (GI). The GI has four layers that make the GI wall where food passes threw, the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and the serosa. Mouth: The primary function of the mouth and its components is to divide food into smaller pieces and then force it from the mouth into the esophagus. The mouth consists of the hard palate, nasopharynx passage, soft palate, epiglottis and glottis, and the trachea. When you swallow food is pushed to the back of the throat by the tongue. When the food slides down the esophagus the other passageways are blocked off to prevent food from going where it should not.
Mouth: The primary function of the mouth and its components is to divide food into smaller pieces and then force it from the mouth into the esophagus. The mouth consists of the hard palate, nasopharynx passage, soft palate, epiglottis and glottis, and the trachea. When you swallow food is pushed to the back of the throat by the tongue. When the food slides down the esophagus the other passageways are blocked off to prevent food from going where it should not.Pharynx: Is the passageway that food enters when it is swallowed and the intermediary between the mouth and the esophagus.
 Esophagus: the esophagus connects the food being broken down in the mouth to the stomach where it first begins to be chemically broken down. The esophagus is a long tube in the body where the wall can constrict when you swallow and force food down the stomach called the peristaltic wave.
Esophagus: the esophagus connects the food being broken down in the mouth to the stomach where it first begins to be chemically broken down. The esophagus is a long tube in the body where the wall can constrict when you swallow and force food down the stomach called the peristaltic wave. Stomach: The stomach organ sits right below the diaphragm and is the first stop of the food in the lower body. The stomach consits of the usual four layers of the GI but has modifications to the muscularis layer as well as another layer which allows the stomach to expand and contract. In stomach contains the pyloric sphincter which blocks food from leaving the stomach until it has been processed enough for the next stage. The stomach fluid is made mostly of chyme which helps control the breakdown of food.
Stomach: The stomach organ sits right below the diaphragm and is the first stop of the food in the lower body. The stomach consits of the usual four layers of the GI but has modifications to the muscularis layer as well as another layer which allows the stomach to expand and contract. In stomach contains the pyloric sphincter which blocks food from leaving the stomach until it has been processed enough for the next stage. The stomach fluid is made mostly of chyme which helps control the breakdown of food.Small intestine: The small intestine has a smaller diameter then the large intestine but the is much longer then the large intestine. In the small intestine the digestion of food by the enzymes secreated by the pancreas and bile form the gallbladder make quick work of the food particles. The small intestine wall also absorbs nutrients mainly sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, and glycerol for the digestive process.
Obesity and Cardiovascular disease: When people eat to much sweets which are high in surgar and fats from fried food it can lead to being obese with the additional threat of diabetes type 2 and cardiovascular disease. In diabetes the cells get so much sugar from what you eat the body produces to much insulin to break down the sugar. Over time the cells get so immune to the effects of the insulin they stop recognizing and responding the insulin diabetes is the result. They you have to inject insulin into the body to get the cells to recognize it and use it for breaking down sugars in your diet.
Accessory Organs: Pancreas, Liver, Gall bladder.
Pancreas: The pancreas uses the duodenum to deliver pancreatic juice with digestive enzymes for all types of food. Insulin is produced by the pancreas when the body needs extra to handle the sugar intake, insulin is a hormone (substance produced by one set of cells which affects another set of cells).
Pancreas: The pancreas uses the duodenum to deliver pancreatic juice with digestive enzymes for all types of food. Insulin is produced by the pancreas when the body needs extra to handle the sugar intake, insulin is a hormone (substance produced by one set of cells which affects another set of cells).
Liver: The liver is primarily used to detoxify the blood and remove any poisonous substances (like beer). Since the liver acts as a sewage plant for the body it is one of the largest major metabolic glands in the body. If the liver fails it can be life threatening to the person, and a transplant is generally needed. The liver does have amazing rebuilding capabilities, but when the rate of damage is faster then what the liver can repair you have a serious problem.
Gall bladder: The gall bladders major function is to store bile to be used in the liver and other organs. Bile breaks down fats into smaller pieces which make it easier to digest by other enzymes. If the bile in the gall bladder hardens into gallstones it can be incredibly painful until they are forced out of the body.
Gall bladder: The gall bladders major function is to store bile to be used in the liver and other organs. Bile breaks down fats into smaller pieces which make it easier to digest by other enzymes. If the bile in the gall bladder hardens into gallstones it can be incredibly painful until they are forced out of the body.
 Large intestine: The large intestine is composed of the cecum, colon, rectum and anal canal. The cecum is the first part of the large intestine and the entry point for defecation. The colon has three major parts, the ascending colon, transverse colon, and the descending colon. These three parts of the colon give it the box shape outline around the other organs. The large intestine form feces using fiber and other components. Feces are unproved parts of food we ingest and need to leave the body, for a person to stay healthy. Feces will collect in the rectum until a signal is sent to the brain to loosen the rectum and allow the feces to exit out the anus. One more note since feces are three quarters water to one part solid if you have diarrhea for an extended period of time you are dehydrating your body and will need to keep drinking fluids to prevent the problem from getting worse.
Large intestine: The large intestine is composed of the cecum, colon, rectum and anal canal. The cecum is the first part of the large intestine and the entry point for defecation. The colon has three major parts, the ascending colon, transverse colon, and the descending colon. These three parts of the colon give it the box shape outline around the other organs. The large intestine form feces using fiber and other components. Feces are unproved parts of food we ingest and need to leave the body, for a person to stay healthy. Feces will collect in the rectum until a signal is sent to the brain to loosen the rectum and allow the feces to exit out the anus. One more note since feces are three quarters water to one part solid if you have diarrhea for an extended period of time you are dehydrating your body and will need to keep drinking fluids to prevent the problem from getting worse. Obesity: The body mass index (BMI) is used to calculate a persons body fat to tell if they are at a healthy BMI or at risk for being obese. Studies have shown there is a global problem with people and children becoming obese (globosity).
Obesity: The body mass index (BMI) is used to calculate a persons body fat to tell if they are at a healthy BMI or at risk for being obese. Studies have shown there is a global problem with people and children becoming obese (globosity).Nutrients: Are components are body uses for a variety of different purposes. Energy, growth and development and cellular metabolism. Carbohydrates (sugars), proteins (amino acids), and lipids (fats, oils, cholesterol) are all nutrients which have a physiological function in the body.
Minerals: The body needs about 5 grams of each major mineral and less then 5 grams for trace minerals. Major minerals are calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chloride, and magnesium. For all minerals just like nutrients too much of any one can have negative affects on the body as with have not enough. The trace minerals are zinc, iron, copper, iodine, selenium, manganese.
Vitamins: There are 13 essential vitamins which are important to the body because we can not produce enough of them on our own, they must be included in our diet. Vitamins are organic compounds which are not carbs, fat, or protein which are body also needs constantly. Having to very little of certain vitamins can vitamin deficiency problems, likewise having to much vitamins can also be bad for you.
No comments:
Post a Comment